
AG Bröring
Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Ruth Bröring
Medical Research Centre
Gastro MFZ, 1rst Floor
Chronic liver diseases are caused by continuous or repeated damage to the liver, leading to fibrosis and cirrhosis, representing inflammatory and scarring processes, respectively. A variety of etiologies, such as viral infection, toxin exposure, alcohol abuse, metabolic and genetic diseases are associated with persistent liver injury, harbouring the risk for hepatocellular carcinogenesis.
Our team has developed an all-in-one liver cell preparation technique from human tissue, allowing analysis of cell type-specific, liver-specific and disease-specific aspects on cellular and molecular levels. The parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells of the liver are part of the innate immune system. They express evolutionarily highly conserved inheritable factors called pathogen recognition receptors (PRRs). They recognize molecular patterns of viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites that are absent in higher organisms. However, damage associated molecular pattern are recognized as well, suggesting a vital role in chronic liver diseases. The PRR represent one of the first lines of defence against invading pathogens and mediate a coordinated immune response through the expression of inflammatory cytokines, antiviral factors, and chemotactic agents.
Disease-related imbalance of the hepatic immune system affects I) growth and regeneration controlled by Hippo signalling pathway, II) functions of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus and III) autophagy and vesicular transport. The major goal of our research is to reveal pathophysiological processes at the molecular level in order to monitor the progression of chronic liver diseases and improve therapies.
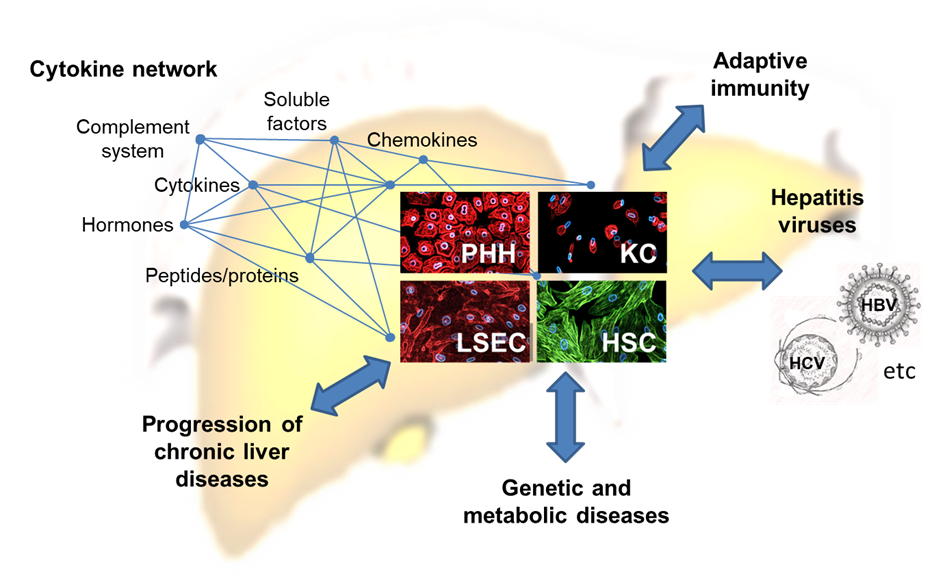
… the influence of parenchymal and non-parenchymal liver cells on hepatitis B virus infection and how virus-host interactions determine immunopathology and chronicity.
… the role of HBe and HBs antigens in evading endogenous innate immune responses using models of hepatitis B virus infection.
… how HBs antigen induces stress in the endoplasmic reticulum, impairs autophagy processes, and promotes proliferation and hepatocarcinogenesis.
… multimolecular therapeutic strategies against copper overload in Wilson disease (WilsonMed).
… the effects of Wilson disease on innate signaling, Hippo pathway activity, and intracellular transport in a cell culture model.
- Luo X, Zhang R, Schefczyk S, Liang Y, Lin SS, Liu S, Baba HA, Lange CM, Wedemeyer H, Lu M, Broering R. Nuclear translocation of YAP drives BMI1-associated hepatocarcinogenesis in hepatitis B virus infection. Liver Int. 2023 Jun 14. doi: 10.1111/liv.15628. Online ahead of print.
- Schrader JA, Burkard TL, Brüggemann Y, Gömer A, Meister TL, Fu RM, Mehnert AK, Dao Thi VL, Behrendt P, Durantel D, Broering R, Vondran FWR, Todt D, Kinast V, Steinmann E. EGF receptor modulates HEV entry in human hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2023 Jun 1;77(6):2104-2117.
- Meister TL, Brüggemann Y, Nocke MK, Ulrich RG, Schuhenn J, Sutter K, Gömer A, Bader V, Winklhofer KF, Broering R, Verhoye L, Meuleman P, Vondran FWR, Camuzet C, Cocquerel L, Todt D, Steinmann E. A ribavirin-induced ORF2 single-nucleotide variant produces defective hepatitis E virus particles with immune decoy function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Aug 23;119(34):e2202653119.
- Werner M, Schefczyk S, Trippler M, Treckmann JW, Baba HA, Gerken G, Schlaak JF, Broering R. Antiviral toll-like receptor signaling in non-parenchymal liver cells is restricted to TLR3. Viruses 2022, 14(2), 218.
- Luo X, Zhang R, Lu M, Liu S, Baba HA, Gerken G, Wedemeyer H, Broering R. Hippo pathway counter-regulates innate immunity in Hepatitis B virus infection. Front Immunol. 2021 May 25;12:684424.
- Du Y, Anastasiou OE, Strunz B, Scheuten J, Bremer B, Kraft A, Kleinsimglinhaus K, Todt D, Broering R, Hardtke-Wolenski M, Wu J, Yang D, Dittmer U, Lu M, Cornberg M, Björkström NK, Khera T, Wedemeyer H. The impact of hepatitis B surface antigen on natural killer cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Liver Int. 2021 Sep;41(9):2046-2058.
- Zhou L, He R, Fang P, Li M, Yu H, Wang Q, Yi Y, Wang F, Zhang Y, Chen A, Peng N, Lin Y, Zhang R, Trilling M, Broering R, Lu M, Zhu Y, Liu S. Hepatitis B Virus rigs the cellular metabolome to avoid innate immune recognition. Nat Commun. 2021 Jan 4;12(1):98.
- Kinast V, Plociennikowska A, Anggakusuma, Bracht T, Todt D, Brown RJP, Boldanova T, Zhang Y, Brüggemann Y, Friesland M, Engelmann M, Vieyres G, Broering R, Vondran FWR, Heim MH, Sitek B, Bartenschlager R, Pietschmann T, Steinmann E. C19orf66 is an interferon-induced inhibitor of HCV replication restricting formation of the viral replication organelle. J Hepatol. 2020 Sep;73(3):549-558.
- Zhang Z , Trippler M, Real CI, Werner M, Luo X, Schefczyk S, Kemper T , Anastasiou OE, Ladiges Y, Treckmann J, Paul A, Baba HA, Allweiss L, Dandri M, Gerken G, Wedemeyer H, Schlaak JF, Lu M, Broering R. Hepatitis B Virus Particles Activate Toll-Like Receptor 2 Signaling Initially Upon Infection of Primary Human Hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2020 Sep;72(3):829-844.
- Yu H, Li M, He R, Fang P, Wang Q, Yi Y, Wang F, Zhou L, Zhang Y, Chen A, Peng N, Lu M, Trilling M, Broering R, Zhu Y, Liu S. Major vault protein promotes hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting interferon regulatory factor 2 and decreasing p53 activity. Hepatology 2020 Aug;72(2):518-534.
Mitarbeiter

Dr. rer. nat.
Stefan Schefczyk
M.Sc. Biologie, AG Bröring

Caini Yang
cand. Dr. med., Doktorandin, AG Bröring

Martha-Julia Sasula
M. Sc. Molekulare Zellbiologie, AG Bröring

Lorraine Tendai Muungani
M.Sc. Biologie, AG Bröring

Anna Held
cand. Dr. med., Doktorandin, AG Bröring

Prof. Dr. rer. nat.
Ruth Bröring
Diplom Biologin, Laborleitung
